A CDN is the same as a web host, isn’t it
By utilizing caching to scale back hosting information bandwidth, serving to stop interruptions in service, and improving security, CDNs are a well-liked option to relieve a number of the most important pain points that go with ancient internet hosting.
Why isn’t a CDN a Default Part of my Website Hosting
Today things have been modified and plenty of hosting providers really do supply CDN services as a checkbox add-on.
What are the advantages of using a CDN
Improving website load times – By distributing content closer to website guests by employing a close CDN server (among other optimizations), visitors experience faster page loading times. As visitors are more inclined to click away from a slow-loading website, a CDN will decrease rates and increase the quantity of your time that visitors pay on the site. In other words, a faster website means that a lot visitors can keep and stick around longer.
Reducing bandwidth prices – Bandwidth consumption prices for website hosting could be a primary expense for websites. Through caching and alternative optimizations, CDNs are ready to cut back the quantity of data an origin server must provide, therefore reducing hosting prices for website owners.
Improving website security – A CDN might improve security by providing DDoS mitigation, enhancements to security certificates, and alternative optimizations.
How a CDN works
These Internet exchange points (IXPs) are the first locations where different Internet providers connect so as to supply one another access to traffic originating on their different networks. By having a connection to that high speed and extremely interconnected locations, a CDN supplier is ready to reduce prices and transit times in high-speed data delivery.
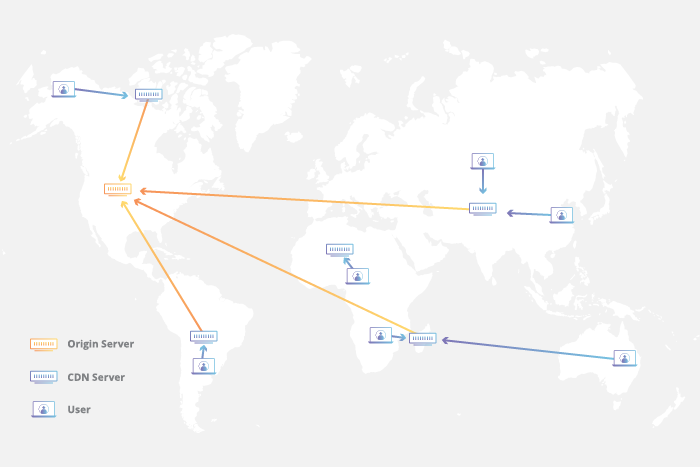
Latency - How can a CDN improve website load times
Whenever it comes to websites loading content, users drop off immediately as a website slows down. CDN services can facilitate to reduce load times in the following ways:
The globally distributed nature of a CDN describes the reduction of the distance between users and website resources. Rather than having to connect to wherever a website’s origin server might live, a CDN lets users connect with a geographically closer information center. Less travel period means quicker service.
The ways a CDN helps websites load faster
I intelligent failover provides uninterrupted service if one or additional of the CDN servers will go offline because of hardware malfunction; the failover will distribute the traffic to the opposite operational servers.
Evolution of CDN’s
Commercial CDNs are around since the ’90s. Like all different decades-old technology, they went through many evolutionary stages before changing into the strong application delivery platform they’re nowadays.
The path of CDN development was formed by an economic process, as well as new trends in content consumption and large connectivity advancements. The latter has been enabled by fiber optics and different new communication technologies.
According to Hostt overall, CDN evolution will be divided into 3 generations, everyone introducing new capabilities, technologies and ideas to its network architecture. Working in parallel, every generation saw the evaluation of CDN services trend down, marking its transformation into a mass-market technology.

So what a CDN is going to do for me.
- Improve page load speed
- Handle high traffic loads
- Handle high traffic loads
- Localize coverage while not the price
- Reduce information consumption
- Load balance between several servers
- Protect your website from DDoS attacks
- Secure your application
- And more
